Data Interpretation is related to the understanding, organizing as well as interpretation of data to arrive at a meaningful answer. With a piece of information being provided, questions are required to be solved based on the data.
In the case of bank exams, around 10-15 questions are asked in prelims and around 10 to 20 questions are asked in the mains examination. The list of exams includes SBI PO, IBPS PO, IBPS RRB, LIC AAO, SSC CGL, SBI Clerk, IBPS Clerk, IBPS SO etc. Good command over topics of numerical ability is important to solve these types of questions.
Data Interpretation PDF
Data interpretation PO Mains PDF Set 1
Data Interpretation PO Mains PDF set 2
Data Interpretation Clerk Mains PDF Set 3
Caselet Data Interpretation PDF Set 5
Data Interpretation Clerk Mains PDF Set 4
Bar Charts
Pie Charts
Table Charts
Mixed Charts
Line Chart
Web Chart
Set Theory
Info chart
Data Interpretation can be one of the most time-consuming topics in the Quantitative Aptitude section of bank examinations. Some of the reasons why data interpretation is not among the favourites of students include the following:
- Questions related to Data interpretation can be confusing and candidates might be confused about the information related to a table or illustration.
- A lack of familiarity related to tables or graphs can result in the candidates skipping the question.
- It requires mastery of multiple topics which includes questions from percentages, averages, ratio and proportion, and mixture & allegation.
Format of Data Interpretation Questions
The questions based on Data Interpretation can be asked in various formats. Some of the formats in which questions can be asked in prelims and mains include the following:
- Bar Graph – In this case, the Information can be presented in the format of bar graph format and questions based on it are required to be answered.
- Pie Chart – A pie chart depicts a circular representation of data. The info can be one or more pie charts in a question.
- Missing Data – The missing data format is where you are required to compute the missing information and then solve the given questions.
- Tabular Form – Data is presented in the form of a table and interpreting the data is required in order to solve the questions.
- Line Chart – A line chart represents data in the form of a line or linear format. Such type of questions is commonly asked in bank exams.
- Caselet DI – A caselet is statement based data. There is no depiction of an image. One needs to read the paragraph thoroughly and then move on to solve the questions
Solving questions based on DI
The following factors should be taken into consideration while solving questions based on data interpretation.
Write down the list of topics which are important to master questions related to DI. The topics include Averages, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion and Mixture & Allegation.
Jot all the important formulas for each of the topics.
Ratio = Comparing values in the form ‘p/q’ to find out their simplest terms
Averages = (Sum of Values) / (Total Number of Values)
Percentage = (Number/Total Numbers) * 100
Percentage Change = [(New Value – Old Value) / Old Value] * 100
Understand the requirements for each of the DI questions. It includes - linear graphs, bar graphs, pie graphs, tables and mixed graphs.
Along with writing each kind of graph, note the example question to learn more about solving them.
Read and understand the question carefully, learn to understand what the graph suggests.
Understand the time required to solve such questions and learn to avoid such questions if they are too time-consuming.
High Level DI Questions for Bank PO like SBI and IBPS PO Mains,
Directions : Study the following line chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
A battery is sold by four different shops A, B, C and D. The chart given below shows the percentage of discount offered by each shop for in three different years 2015, 2016 and 2017. Marked price, as well as the cost price of the battery, is the same for each shop in a particular year unless mentioned otherwise.
.png) |
Questions :
1. Marked price of battery increases by 20% every year with respect to previous year. Average of marked price of battery for the year 2014, 2015 and 2016 is Rs. 1820. Profit percent earned by shop D on selling a battery in 2017 was 38.24%. Find the difference between profit percentage of shop B and C in 2015 if cost price of battery increases by Rs. 150 with respect to previous year.
A. 12%
B. 10%
C. 15%
D. 20%
E. 16%
Solution : C
Let marked price of battery in 2014 was Rs. x
Marked price of battery in 2015 was 120% of x = Rs. 1.2x
Marked price of battery in 2016 was 120% of 1.2x = Rs. 1.44x
3.64x = 5460
x = 1500
Marked price of battery in 2017 = 120% of 1.44x = 1.728x = Rs. 2592
Selling price of battery at shop D in 2017 = 80% of 2592 = Rs. 2073.6
Let cost price of battery in 2017 was Rs. y
So y + 38.24% of y = 2073.6
Cost price of battery in 2015 = 1500 – 150 – 150 = Rs. 1200
Marked price of battery in 2015 = 1.2x = Rs. 1800
For shop B in 2015:
Selling price = 75% of 1800 = Rs. 1350
For shop C in 2015:
Selling price = 85% of 1800 = Rs. 1530
Difference in profit percentage = 27.5 – 12.5 = 15%
Hence, option C is correct.
2. Profit earned by shop C each year was same. Increase in marked price of battery from 2016 to 2017 was twice the increase in marked price of battery from 2015 to 2016. Both selling price and cost price for shop C increased by Rs. 100 from 2016 to 2017. Battery is marked up Rs. 700 and Rs. 1600 above the cost price in 2016 and 2017 respectively. What is the profit earned by shop A in 2015?
A. Rs. 120
B. Rs. 100
C. Rs. 140
D. Rs. 50
E. Rs. 200
Solution : B
Let marked price of battery in 2015 was Rs. x
Increase in marked price of battery in 2016 from 2015 was Rs. y
Marked price of battery in 2016 = Rs. (x + y)
According to question:
Increase in marked price of battery in 2017 from 2016 was Rs. 2y
Marked price of battery in 2017 = Rs. (x + y + 2y) = Rs. (x + 3y)
Let selling price of battery in 2016 was Rs. b
Selling price of battery in 2017 was Rs. (b + 100)
Selling price of battery in 2016 = 80% of (x + y)
Selling price of battery in 2017 = 60% of (x + 3y)
So 80% of (x + y) = b -------(1)
And 60% of (x + 3y) = b + 100
60% of (x + 3y) – 100 = b -----(2)
From (1) and (2)
0.8x + 0.8y = 0.6x + 1.8y – 100
y – 0.2x = 100
Let cost price of battery in 2016 was Rs. a
Cost price of battery in 2017 was Rs. (a + 100)
Marked cost price of battery in 2016 = Rs. (a + 700)
Marked cost price of battery in 2017 = Rs. (a + 100 + 1600) = Rs. (a + 1700)
So x + y = a + 700
x + y – 700 = a -----(3)
And x + 3y = a + 1700
x + 3y – 1700 = a ----(4)
From (3) and (4)
x + y – 700 = x + 3y – 1700
2y = 1000
y = 500
a = x + y – 700 = 1800
b = 80% of (x + y) = 2000
Profit earned by shop C in 2017 = 2000 – 1800 = Rs. 200
marked price of battery in 2015 = Rs. 2000
Selling price of battery at shop C in 2015 = 85% of 2000 = Rs. 1700
Selling price of battery in 2015 = 1700 – 200 = Rs. 1500
Selling price of battery at shop A in 2015 = 80% of 2000 = Rs. 1600
Profit earned by shop A in 2015 = 1600 – 1500 = Rs. 100
Hence, option B is correct.
3. Ratio of cost price of battery in 2015:2016:2017 was 2:4:5. Ratio of selling price at shop D in 2015 :2 016:2017 was 7:12:16. Average of profit earned by A and C in 2016 was Rs. 400 and total profit earned by B in three years is Rs. 970. Find the difference of discount offered by C in 2015 and 2017.
A. Rs. 650
B. Rs. 450
C. Rs. 750
D. Rs. 700
E. Rs. 550
Solution : A
Selling price of battery at shop B in 2016 = 70% of 16y = 11.2y
Selling price of battery at shop B in 2017 = 65% of 20y = 13y
So 7.5y + 11.2y + 13y – 2z – 4z – 5z = 970
31.7y – 11z = 970
31.7y – 11 x (3y – 100) = 970 [from (1)]
31.7y – 33y = 970 – 1100
Discount offered by C in 2017 = 40% of 20y = Rs. 800
Difference = 800 – 150 = Rs. 650
Hence, option A is correct.
4. Marked price in 2017 was Rs. 8000 and marked price in 2016 was same as the selling price at shop A in 2017. Cost price in 2016 was same as the selling price at shop D in 2015. Profit percent earned by A in 2016 was 36%. If cost price in 2015 was Rs. 2295 then find the ratio of profit earned by shop B in 2015 to shop C in 2016.
A. 5 : 8
B. 1 : 3
C. 2 : 3
D. 3 : 4
E. 7 : 9
Solution : D
Marked price in 2016 = 85% of 8000 = Rs. 6800
Selling price at shop A in 2016 = 70% of 6800 = Rs. 4760
Let the cost price in 2016 was Rs. a
So a + 36% of a = 4760
Selling price at shop D in 2015 = Rs. 3500
70% of Marked price in 2015 = 3500
Selling price at shop B in 2015 = 75% of 5000 = Rs. 3750
Profit earned by shop B in 2015 = 3750 – 2295 = Rs. 1455
Selling price at shop C in 2016 = 80% of 6800 = Rs. 5440
Profit earned by shop C in 2016 = 5400 – 3500 = Rs. 1940
Ratio = 1455 : 1940 = 3 : 4
Hence, option D is correct.
5. Selling price at shop B in 2015 and 2016 was Rs. 2400 and Rs. 2800 respectively and selling price at shop D in 2017 was Rs. 3840. Ratio of profit earned by A to C in 2016 was 2:3. If cost prices were in an increasing AP with passing years with a common difference of Rs. 400, find the difference between profit earned by A in 2015 and in 2017.
A. Rs. 840
B. Rs. 800
C. Rs. 780
D. Rs. 720
E. Rs. 700
Solution: D
75% of Marked price in 2015 = 2400
70% of Marked price in 2016 = 2800
80% of Marked price in 2017 = 3840
Selling price at shop A in 2016 = 70% of 4000 = Rs. 2800
Selling price at shop C in 2016 = 80% of 4000 = Rs. 3200
Let profit earned by A and C in 2016 was 2x and 3x respectively
Let cost price in 2016 was Rs. y
So 2800 – 2x = y ------(1)
And 3200 – 3x = y -------(2)
From (1) and (2)
2800 – 2x = 3200 – 3x
x = 400
y = 2800 – 800 = 2000
For A in 2015:
Cost price = Rs. 1600
Selling price = 80% of 3200 = Rs. 2560
Profit earned = 2560 – 1600 = Rs. 960
For A in 2017:
Cost price = Rs. 2400
Selling price = 85% of 4800 = Rs. 4080
Profit earned = 4080 – 2400 = Rs. 1680
Difference = 1680 – 960 = Rs. 720
Hence, option D is correct.
Solution : C
Let marked price of battery in 2014 was Rs. x
Marked price of battery in 2015 was 120% of x = Rs. 1.2x
Marked price of battery in 2016 was 120% of 1.2x = Rs. 1.44x
| So | x + 1.2x + 1.44x | = 1820 |
| 3 |
3.64x = 5460
x = 1500
Marked price of battery in 2017 = 120% of 1.44x = 1.728x = Rs. 2592
Selling price of battery at shop D in 2017 = 80% of 2592 = Rs. 2073.6
Let cost price of battery in 2017 was Rs. y
So y + 38.24% of y = 2073.6
| y = | 2073.6 | × 100 = Rs. 1500 |
| 138.24 |
Cost price of battery in 2015 = 1500 – 150 – 150 = Rs. 1200
Marked price of battery in 2015 = 1.2x = Rs. 1800
For shop B in 2015:
Selling price = 75% of 1800 = Rs. 1350
| Profit % = | 1350 – 1200 | × 100 = 12.5% |
| 1200 |
For shop C in 2015:
Selling price = 85% of 1800 = Rs. 1530
| Profit % = | 1530 – 1200 | × 100 = 27.5% |
| 1200 |
Difference in profit percentage = 27.5 – 12.5 = 15%
Hence, option C is correct.
2. Profit earned by shop C each year was same. Increase in marked price of battery from 2016 to 2017 was twice the increase in marked price of battery from 2015 to 2016. Both selling price and cost price for shop C increased by Rs. 100 from 2016 to 2017. Battery is marked up Rs. 700 and Rs. 1600 above the cost price in 2016 and 2017 respectively. What is the profit earned by shop A in 2015?
A. Rs. 120
B. Rs. 100
C. Rs. 140
D. Rs. 50
E. Rs. 200
Solution : B
Let marked price of battery in 2015 was Rs. x
Increase in marked price of battery in 2016 from 2015 was Rs. y
Marked price of battery in 2016 = Rs. (x + y)
According to question:
Increase in marked price of battery in 2017 from 2016 was Rs. 2y
Marked price of battery in 2017 = Rs. (x + y + 2y) = Rs. (x + 3y)
Let selling price of battery in 2016 was Rs. b
Selling price of battery in 2017 was Rs. (b + 100)
Selling price of battery in 2016 = 80% of (x + y)
Selling price of battery in 2017 = 60% of (x + 3y)
So 80% of (x + y) = b -------(1)
And 60% of (x + 3y) = b + 100
60% of (x + 3y) – 100 = b -----(2)
From (1) and (2)
0.8x + 0.8y = 0.6x + 1.8y – 100
y – 0.2x = 100
Let cost price of battery in 2016 was Rs. a
Cost price of battery in 2017 was Rs. (a + 100)
Marked cost price of battery in 2016 = Rs. (a + 700)
Marked cost price of battery in 2017 = Rs. (a + 100 + 1600) = Rs. (a + 1700)
So x + y = a + 700
x + y – 700 = a -----(3)
And x + 3y = a + 1700
x + 3y – 1700 = a ----(4)
From (3) and (4)
x + y – 700 = x + 3y – 1700
2y = 1000
y = 500
| x = | y – 100 | = 2000 |
| 0.2 |
a = x + y – 700 = 1800
b = 80% of (x + y) = 2000
Profit earned by shop C in 2017 = 2000 – 1800 = Rs. 200
marked price of battery in 2015 = Rs. 2000
Selling price of battery at shop C in 2015 = 85% of 2000 = Rs. 1700
Selling price of battery in 2015 = 1700 – 200 = Rs. 1500
Selling price of battery at shop A in 2015 = 80% of 2000 = Rs. 1600
Profit earned by shop A in 2015 = 1600 – 1500 = Rs. 100
Hence, option B is correct.
3. Ratio of cost price of battery in 2015:2016:2017 was 2:4:5. Ratio of selling price at shop D in 2015 :2 016:2017 was 7:12:16. Average of profit earned by A and C in 2016 was Rs. 400 and total profit earned by B in three years is Rs. 970. Find the difference of discount offered by C in 2015 and 2017.
A. Rs. 650
B. Rs. 450
C. Rs. 750
D. Rs. 700
E. Rs. 550
Solution : A
Let cost price of battery in 2015, 2016 and 2017 was Rs. 2z, Rs. 4z and Rs. 5z respectively, and
Selling price of battery at shop D in 2015, 2016 and 2017 was Rs. 7y, Rs. 12y and Rs. 16y respectively.
70% of Marked price of battery in 2015 = Rs. 7y
Marked price of battery in 2015 = Rs. 10y
Similarly,
Marked price of battery in 2016 = Rs. 16y
Marked price of battery in 2017 = Rs. 20y
Selling price of battery at shop A in 2016 = 70% of 16y = 11.2y
Selling price of battery at shop C in 2016 = 80% of 16y = 12.8y
Profit of shop A in 2016 = 11.2y – 4z
Profit of shop C in 2016 = 12.8y – 4z
So 11.2y – 4z + 12.8y – 4z = 400 × 2
24y – 8z = 800
3y – z = 100 ----------(1)
Selling price of battery at shop B in 2015 = 75% of 10y = 7.5y
Selling price of battery at shop B in 2016 = 70% of 16y = 11.2y
Selling price of battery at shop B in 2017 = 65% of 20y = 13y
So 7.5y + 11.2y + 13y – 2z – 4z – 5z = 970
31.7y – 11z = 970
31.7y – 11 x (3y – 100) = 970 [from (1)]
31.7y – 33y = 970 – 1100
1.3y = 130
y = 100
z = 200
Discount offered by C in 2015 = 15% of 10y = Rs. 150
Discount offered by C in 2017 = 40% of 20y = Rs. 800
Difference = 800 – 150 = Rs. 650
Hence, option A is correct.
4. Marked price in 2017 was Rs. 8000 and marked price in 2016 was same as the selling price at shop A in 2017. Cost price in 2016 was same as the selling price at shop D in 2015. Profit percent earned by A in 2016 was 36%. If cost price in 2015 was Rs. 2295 then find the ratio of profit earned by shop B in 2015 to shop C in 2016.
A. 5 : 8
B. 1 : 3
C. 2 : 3
D. 3 : 4
E. 7 : 9
Solution : D
Marked price in 2016 = 85% of 8000 = Rs. 6800
Selling price at shop A in 2016 = 70% of 6800 = Rs. 4760
Let the cost price in 2016 was Rs. a
So a + 36% of a = 4760
| a = | 4760 | = Rs. 3500 |
| 1.36 |
Selling price at shop D in 2015 = Rs. 3500
70% of Marked price in 2015 = 3500
| Marked price in 2015 = | 3500 | = Rs. 5000 |
| 0.7 |
Selling price at shop B in 2015 = 75% of 5000 = Rs. 3750
Profit earned by shop B in 2015 = 3750 – 2295 = Rs. 1455
Selling price at shop C in 2016 = 80% of 6800 = Rs. 5440
Profit earned by shop C in 2016 = 5400 – 3500 = Rs. 1940
Ratio = 1455 : 1940 = 3 : 4
Hence, option D is correct.
5. Selling price at shop B in 2015 and 2016 was Rs. 2400 and Rs. 2800 respectively and selling price at shop D in 2017 was Rs. 3840. Ratio of profit earned by A to C in 2016 was 2:3. If cost prices were in an increasing AP with passing years with a common difference of Rs. 400, find the difference between profit earned by A in 2015 and in 2017.
A. Rs. 840
B. Rs. 800
C. Rs. 780
D. Rs. 720
E. Rs. 700
Solution: D
75% of Marked price in 2015 = 2400
| Marked price in 2015 = | 2400 | = Rs. 3200 |
| 0.75 |
70% of Marked price in 2016 = 2800
| Marked price in 2016 = | 2800 | = Rs. 4000 |
| 0.7 |
80% of Marked price in 2017 = 3840
| Marked price in 2017 = | 3840 | = Rs. 4800 |
| 0.8 |
Selling price at shop A in 2016 = 70% of 4000 = Rs. 2800
Selling price at shop C in 2016 = 80% of 4000 = Rs. 3200
Let profit earned by A and C in 2016 was 2x and 3x respectively
Let cost price in 2016 was Rs. y
So 2800 – 2x = y ------(1)
And 3200 – 3x = y -------(2)
From (1) and (2)
2800 – 2x = 3200 – 3x
x = 400
y = 2800 – 800 = 2000
For A in 2015:
Cost price = Rs. 1600
Selling price = 80% of 3200 = Rs. 2560
Profit earned = 2560 – 1600 = Rs. 960
For A in 2017:
Cost price = Rs. 2400
Selling price = 85% of 4800 = Rs. 4080
Profit earned = 4080 – 2400 = Rs. 1680
Difference = 1680 – 960 = Rs. 720
Hence, option D is correct.
DI for Bank Exam.
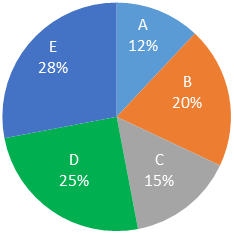
Directions : Study the following pie chart and line chart carefully and answer the questions given beside.
A, 18 : 11
The pie chart shows the number of students study in five different schools as percentage of total number of students study in all five schools A, B, C, D and E. All the students of the schools are divided in two houses Red and Green. Total student in all five schools is 15000.
Questions :
1. If ratio of number of girls in green house to red house in school B is 16:17 then find difference between number of boys and girls in green house.
Solution : D
Total students = 20% of 15000 = 3000
Total girls = 1650
Total boys = 3000 – 1650 = 1350
Boys in red house = 720
Boys in green house = 1350 – 720 = 630
Difference = 800 – 630 = 170
Hence, option D is correct.
2. What is the ratio of girls in red house to green house in school C if total number of students in green house of school C is 1083?
Percentage of students
The line graph shows the number of girls and number of boys who are in red house in each of the five schools.
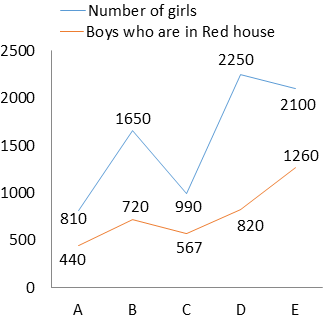

The line graph shows the number of girls and number of boys who are in red house in each of the five schools.

Questions :
1. If ratio of number of girls in green house to red house in school B is 16:17 then find difference between number of boys and girls in green house.
A. 140
B. 180
C. 120
D. 170
E. 210
Solution : D
Total students = 20% of 15000 = 3000
Total girls = 1650
Total boys = 3000 – 1650 = 1350
Boys in red house = 720
Boys in green house = 1350 – 720 = 630
| Girls in green house = | 1650 | × 16 = 800 |
| 33 |
Difference = 800 – 630 = 170
Hence, option D is correct.
2. What is the ratio of girls in red house to green house in school C if total number of students in green house of school C is 1083?
B. 11 : 5
C. 20 : 13
D. 24 : 19
E. 10 : 3
Solution : C
For school C:
Total students = 15% of 15000 = 2250
Total girls = 990
Total boys = 2250 – 900 = 1260
Boys in red house = 567
Boys in green house = 1260 – 567 = 693
Girls in green house = 1083 – 690 = 390
Girls in red house = 990 – 390 = 600
Ratio = 600 : 390 = 20 : 13
Hence, option C is correct.
3. Number of boys in green house of school A is what percent of number of girls in green house of school A if total students in red house of school A is 750?
A. 110%
B. 120%
C. 90%
D. 70%
E. 150%
Solution: A
For school A:
Total students = 12% of 15000 = 1800
Total girls = 810
Total boys = 1800 – 810 = 990
Boys in red house = 440
Boys in green house = 990 – 440 = 550
Girls in red house = 750 – 440 = 310
Girls in green house = 810 – 310 = 500
Hence, option A is correct.
Hence, option C is correct.
3. Number of boys in green house of school A is what percent of number of girls in green house of school A if total students in red house of school A is 750?
A. 110%
B. 120%
C. 90%
D. 70%
E. 150%
Solution: A
For school A:
Total students = 12% of 15000 = 1800
Total girls = 810
Total boys = 1800 – 810 = 990
Boys in red house = 440
Boys in green house = 990 – 440 = 550
Girls in red house = 750 – 440 = 310
Girls in green house = 810 – 310 = 500
| Percentage = | 550 | × 100 = 110% |
| 500 |
Hence, option A is correct.
4. What is the total number of students in red house of school E if number of girls in green house of school E is 1155?
A. 2245
B. 2205
C. 2285
D. 2175
E. 2255
Solution : B
For school E:
Total students = 28% of 15000 = 4200
Total girls = 2100
Total boys = 4200 – 2100 = 2100
Boys in red house = 1260
Boys in green house = 2100 – 1260 = 840
Girls in red house = 2100 – 1155 = 945
Total students in red house = 1260 + 945 = 2205
Hence, option B is correct.
5. What percent of girls are in green house out of total girls of school D if number of girls in red house of school D is 305 more than the boys in same house?
A. 40%
B. 50%
C. 20%
D. 60%
E. 80%
Solution : B
For school D:
Total students = 25% of 15000 = 3750
Total girls = 2250
Total boys = 3750 – 2250 = 1500
Boys in red house = 820
Boys in green house = 1500 – 820 = 680
Girls in red house = 820 + 305 = 1125
Girls in green house = 2250 – 1125
| Percentage = | 1125 | × 100 = 50% |
| 2250 |
Hence, option B is correct.


